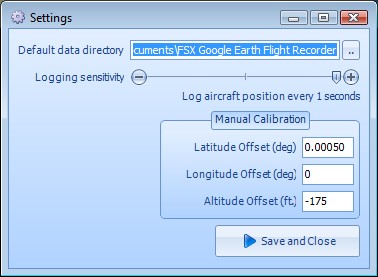
Calibration
Calibration
There is a degree of seperation between the latitude, longitude and altitude between Microsoft Flight Simulator X and Google Earth. For most people, this degree of seperation is not noticable - however if you plan to use FSX Google Earth Flight Recorder to fine tune and analyse your takeoffs, approaches and landings you will need to perform some calibration.
Once calibrated, you will be able to review your flight in immense detail, as close as to within 30cm of the real world Google Earth photography.
Calibration means to make adjustments to the measurements so that they balance correctly. Some calibration has already been done for you, but you may wish to refine and recalibrate for different airfields depending on where you fly most.

If we attempt a take-off, touch and go and landing from Heathrow (EGLL) with these settings, the resulting flight path is as shown:
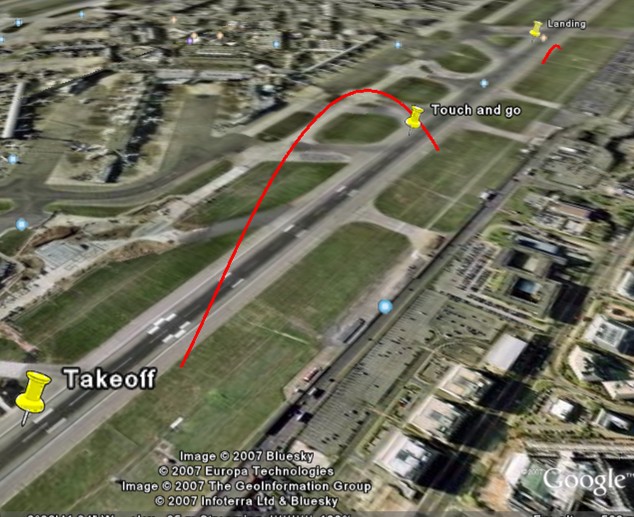
I have placed pushpins to show the approximate position of the real takeoff, touch and go and landing events. The next step is to adjust the values of the latitude, longitude and altitude so that they are correct for the airfield you wish to review.
You need to determine the adjustment to the calibration value that would put your flight path correctly onto the Google Earth image. Adjustments need to be made for Longitude, Latitude and Altitude. I'll show you how to make these adjustments here:
Latitude and Longitude
Position the image so that the flight path is shown top down. With any luck you started on a runway and know exactly where the line should originate. Be aware that if the altitude needs adjustment there is a chance that this line will "pierce" the earth and might not start where you expect it to. We will come to altitude shortly.
Google Earth shows the location of the mouse pointer at any location on the planet. Choose a point on your flightpath (here we choose the bottom of the line) and note down the "Pointer" value. Here: 51,28'39.05N 0,26'22.97W
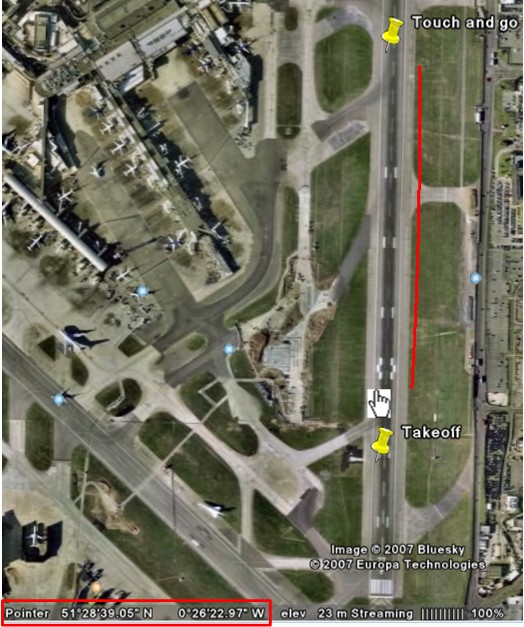

Then hold the pointer over the actual position of the line. Note the value. Here: 51,28'41.39N and 0,26'23.35W.
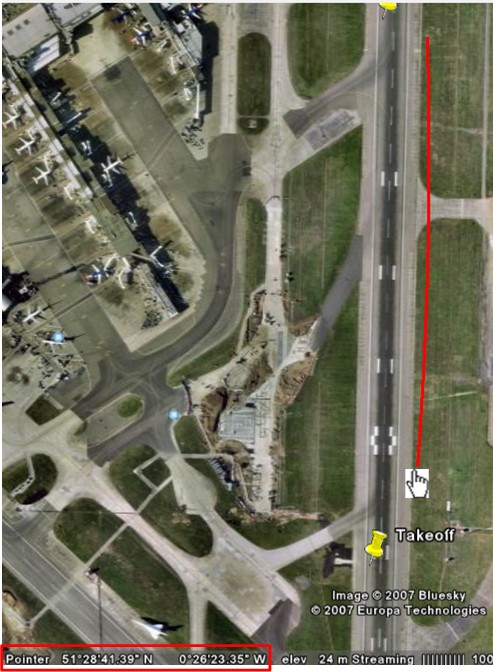

The difference between these values is what you need to adjust the calibration value with.
Target Position: 51,28'39.05N 0,26'22.97W
Actual Line: 51,28'41.39N and 0,26'23.35W
Adjustment: -00000234N (latitude) and -0000038W (longitude)
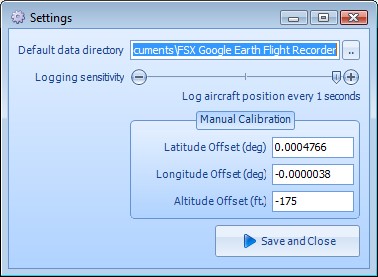
Attempt another flight and compare the lines

Spot on! Now, we have to calculate the adjustment to the altitude.
Swivel Google Earth so that the horizon is visible, together with your take-off line and the runway floor. What we are going to do is draw a line that crosses the base of our flight path to see by how much our flight path is raised off the ground level of Google Earth.
Draw a line in Google Earth, raise the altitude of the line until it meets the base of your flight path, and adjust the altitude calibration by this amount.
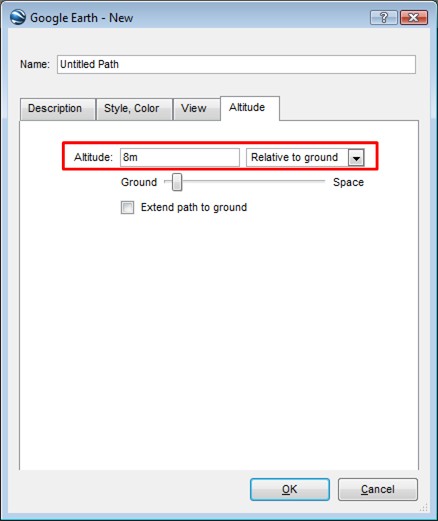
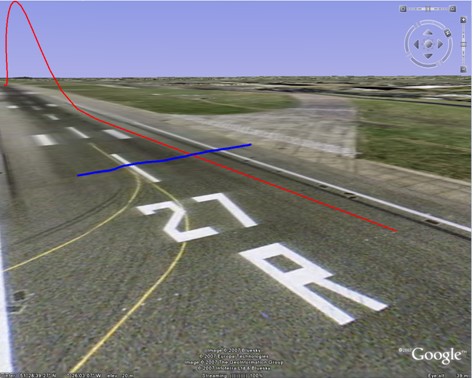
The two lines meet at 6 meters high, according to Google, so we need to apply this to our calibration.
Calibration is complete!
Copyright © 2007, Evolved Software Studios Ltd